
In today’s digital world, security is a top concern for organizations of all sizes. With increasing cyber threats and data breaches, it’s no surprise that businesses are constantly looking for new and innovative ways to protect their sensitive data. One approach that has gained a lot of attention in recent years is the Zero Trust Architecture. This security model challenges the traditional “trust but verify” approach and instead adopts a “never trust, always verify” mindset. But is Zero Trust Architecture just a hyped-up trend or is it truly the future of security? Let’s explore this concept in more detail.

Zero Trust Architecture is a security model that is designed to provide maximum security by assuming that every user, device, and network is untrusted, regardless of their location. This approach requires continuous verification of all entities trying to access an organization’s network or resources, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the network perimeter.
This is in contrast to the traditional security model, where once a user or device gains access to the network, they are considered trusted and can move freely within the network.

The core principle of Zero Trust Architecture is the concept of “least privilege,” which means that only the minimum level of access required for a specific task is granted to a user or device. This is achieved through the implementation of strict access controls, such as multi-factor authentication, network segmentation, and micro-segmentation.
These controls are continuously monitored and enforced to ensure that only authorized entities have access to the network and its resources.
One of the key components of Zero Trust Architecture is the use of identity and access management (IAM) solutions. IAM solutions provide organizations with the ability to manage and control access to their network and resources based on user identity, device identity, and other contextual factors, such as time, location, and behavior.
This allows for a more granular and dynamic approach to access control, ensuring that only the right users, on the right devices, and with the right permissions can access sensitive data.

The primary benefit of Zero Trust Architecture is improved security. By assuming that every entity is untrusted, organizations can greatly reduce the risk of a data breach. This approach also provides better visibility into network activity, allowing for faster detection and response to potential threats. Moreover, the use of IAM solutions can simplify access management and reduce the likelihood of human error, which is often the cause of security incidents.
Zero Trust Architecture also enables organizations to implement a more flexible and scalable security model. With the rise of remote work and cloud-based services, the traditional network perimeter is no longer effective. Zero Trust Architecture allows for secure access to resources from anywhere, without compromising on security.
The short answer is yes. As organizations continue to adopt cloud-based services and allow for remote work, the traditional security model is becoming obsolete. The network perimeter is no longer a reliable defense, and the growing number of cyber threats requires a more dynamic and proactive approach to security.
Zero Trust Architecture provides just that, with its continuous verification and strict access controls. It also aligns with the principles of the “assume breach” mindset, which is becoming increasingly necessary in today’s threat landscape.
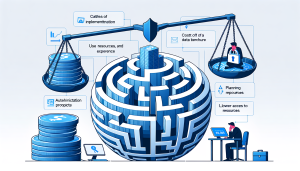
While Zero Trust Architecture offers a more secure and flexible approach to security, it does come with some challenges and considerations. One of the main challenges is the complexity of implementation. Zero Trust Architecture requires a significant amount of planning, resources, and expertise to be implemented effectively. Organizations must also consider the potential impact on user experience, as strict access controls may lead to increased authentication prompts and slower access to resources.
Another consideration is the cost of implementing Zero Trust Architecture. The use of IAM solutions, network segmentation, and other security controls can be expensive, making it challenging for smaller organizations to adopt this model. However, the cost of a data breach far outweighs the cost of implementing Zero Trust Architecture, making it a worthwhile investment for any organization.
Zero Trust Architecture is not just a hyped-up trend; it is the future of security. With its “never trust, always verify” approach, this security model provides organizations with the ability to protect their sensitive data from internal and external threats. While implementing Zero Trust Architecture may come with its challenges, the benefits far outweigh them. As technology continues to evolve, it’s crucial for organizations to adapt their security strategies, and Zero Trust Architecture offers a robust and effective solution for the ever-changing threat landscape.